Hydrocephalus derives from two Greek words ‘hydro’ meaning water and ‘cephalus’ meaning head. This condition occurs when excessive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates in the brain.

Hydrocephalus can be caused by the following conditions:
- A blockage of the CSF flow (within either the ventricles or subarachnoid space)
- A failure of absorbing CSF
- An increased CSF production – very rare


The main symptoms of hydrocephalus are headaches, nausea and vomiting. In addition, there are other age-related symptoms, such as increased head size in babies.
Anatomy review:
Before exploring the different surgical procedures related to Hydrocephalus, it is important to understand the anatomy involved with the CSF production and its flow.
- Choroid plexus: site where CSF is produced. It is formed by the vascularized invaginations of pia mater into ventricles;
- Ventricles: there are 4 ventricles in total – right and left lateral ventricles, 3rd ventricle and 4th ventricle;
- Interventricular foramen (also known as Foramen of Monro): structure that connects the lateral ventricles to the 3rd ventricle;
- Cerebral Aqueduct (also known as Aqueduct of Sylvius): narrow and curved channel that connects the 3rd ventricle to the 4th ventricle. It contains no choroid plexus.

Fig.1 The ventricular system of the human brain (lateral view)

Fig.2 The ventricular system of the human brain (anterior view)

Fig.3 The choroid plexus
Surgical Procedures:
Below some of the surgical procedures related to Hydrocephalus condition are briefly described.
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt: as the name suggests, the catheter that is inserted diverts the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the lateral ventricles of the brain into the peritoneum.

Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV): treatment in which an endoscope is used to puncture a membrane in the floor of the third ventricle creating a pathway for CSF flow within the cavities in the brain.

Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy with Choroid Plexus Cauterization (ETV/CPC): this tretament is similar to the above, with an addition of a of choroid plexus cauterization; only performed in infants.

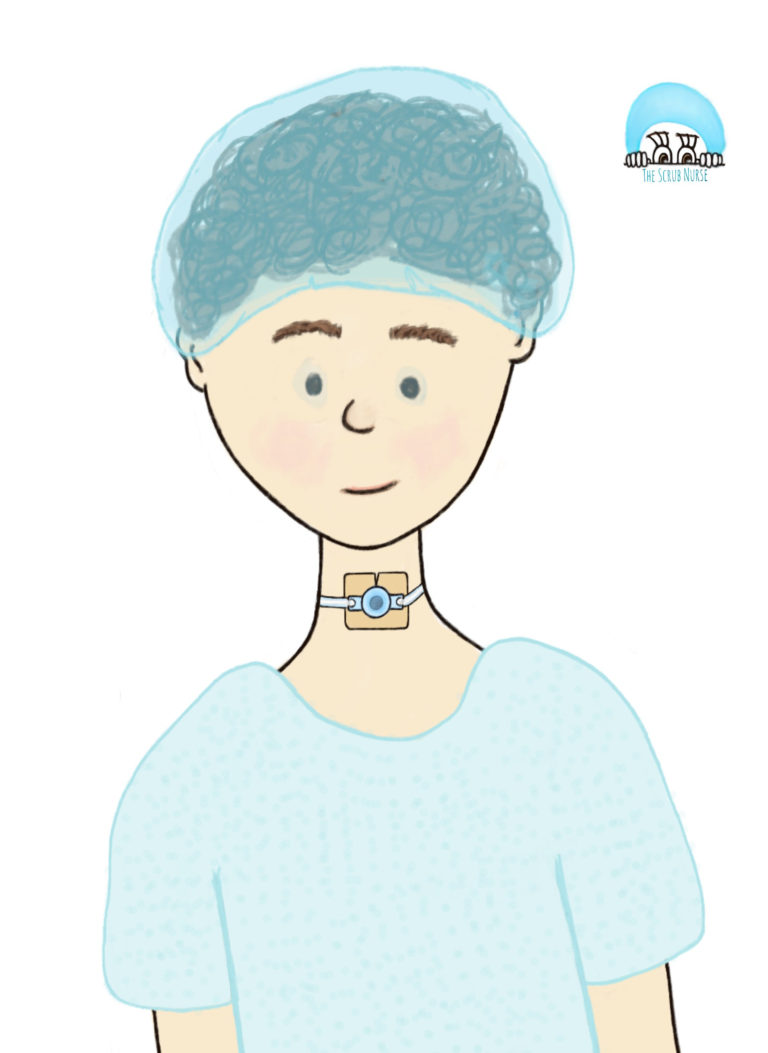
External Ventricular Drainage (EVD): a treatment that allows the temporary drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the ventricles of the brain, relieving raised intracranial pressure.

Intracranial pressure (ICP) bolt: is a monitoring device that measures the intracranial pressure, by inserting a pressure monitor through the skull. It may be indicated after a head injury or post- surgery to the brain.

References:
brainfoundation.org.au – Hydrocephalus
gosh.nhs.uk – evd
gosh.nhs.uk – icp bolt
uhs.nhs.uk – evd
emedicine.medscape.com
hydroassoc.org
neurology.mhmedical.com
kenhub.com


Pingback: Etymological Equation #1 - The Scrub Nurse
Pingback: Fetal surgery for Spina bifida (Myelomeningocele ) – The Scrub Nurse
Pingback: Fetal surgery for Spina bifida (Myelomeningocele ) – The Scrub Nurse