🇬🇧 english version
Did you know that for the infection to occur, all 6 components need to be present. So if you can remove 1 of the links of the Chain of Infection, you can PREVENT infection:
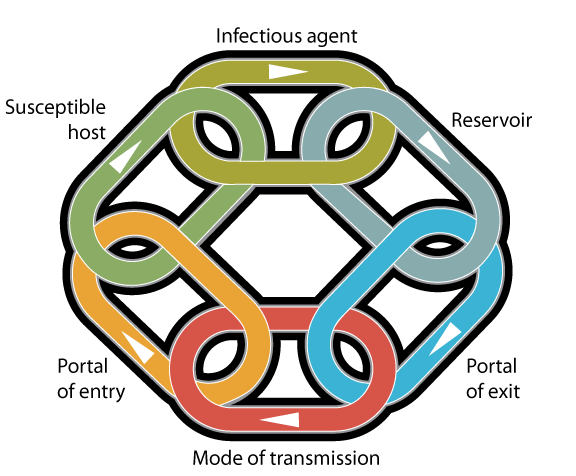
Fig. 1- Chain of Infection, RCN
- Infectious agent / Causative agent – Any microorganism that can produce disease
- Reservoir – a place where the microorganism can live and which provides essential requirements for microorganism’s life. It can be:
- A person (patient, family member or member of staff);
- An inanimate object (such as patient’s furnishings, healthcare equipment, etc).
- Portal of Exit– is the place by which the microorganism escapes from the reservoir. Examples:
- Imagine lots of germs (infectious agent) on top of a medical equipment (reservoir), the healthcare worker manipulates the equipment, her hands are now the portal exit.
- Imagine a person (reservoir) with clostridium difficile (the infectious agent), the loose stools / diarrhea are the path by which microorganisms can escape (portal of exit).
- Mode of transmission – it is how the microorganism spread and move from one place to another. They can use more than one mode of transmission, and there are 5 in total:
- Contact (through skin-to-skin, kissing, sexual intercourse)
- Droplet (by sneezing, coughing, talking)
- Airbone (by dust or droplet nuclei suspended in air)
- Common vehicle (food, water, blood, and inanimate objects – such as handkerchiefs, bedding, surgical scalpels).
- Vector-borne (such as mosquitoes, fleas, and ticks)
- Portal of Entry -is the place by which the microorganism can enter the susceptible host. It is usually the same place as the exit portal.
- Susceptible host – people whose immunitary system is compromised and it does not have the enough mechanisms to fight against mircroorganism transmission. The groups of people more vulnafrable are usually the children, older people, patients immunosuppressed, and malnutrated and dehydrated people.
🇵🇹 versao portuguesa
Sabias que, para que a infecção ocorra, todos os 6 componentes da Cadeia de Infecção precisam de estar presentes? Então, basta removeres um dos links desta para que possas PREVENIR a infecção:
- Agente infeccioso / agente causador – Qualquer microorganismo que pode produzir doença
- Reservatório – um lugar onde o microorganismo pode viver e que fornece requisitos essenciais para a vida do microorganismo. Pode ser:
- Uma pessoa (paciente, familiar ou um profissional de saúde);
- Um objecto inanimado (como mobília do paciente, equipamento de saúde, etc).
- Porta de Saída – o local através do qual o microorganismo escapa do reservatório. Exemplos:
- Imagine imensos germes (agente infeccioso) em cima de um equipamento médico (reservatório), o trabalhador de saúde manipula o equipamento, as mãos dele são agora a porta de saída.
- Imagine uma pessoa (reservatório) com clostridium difficile (o agente infeccioso), as fezes soltas / diarreia são o caminho pelo qual os microorganismos podem escapar (porta de saída).
- Modo de transmissão – é como o microorganismo se espalha e se move de um lugar para outro. Eles podem usar mais de um modo de transmissão e há 5 no total:
- Contacto (através de pele a pele, beijos, relações sexuais)
- Gota (espirrando, tossindo, falando)
- Airbone (por núcleos de poeira ou gotículas suspensos no ar)
- Veículo comum (comida, água, sangue e objectos inanimados – como lenços, roupas de cama, bisturis cirúrgicos).
- Vector (como mosquitos, moscas, pulgas e carrapatos)
- Porta de Entrada – é o local pelo qual o microorganismo pode entrar no hospedeiro susceptível. Geralmente é o mesmo lugar que o portal de saída.
- Hospedeiro susceptível – pessoas cujo sistema imunológico está comprometido e não possuem mecanismos suficientes para combater a transmissão do microrganismo. As pessoas mais vulneráveis geralmente são as crianças, os idosos, os pacientes imunodeprimidos e os desnutridos e desidratados.
References / Referencias:
Royal College of Nursing – Chain of Infection
Surgical Care Made Incredibly Visual!, Chapter 3 – Perioperative Care – Chain of Infection – book
CDC – Section 10: Chain of Infection